


| MOQ: | 1kg |
| Price: | US $15/kg |
| Standard Packaging: | Cylinder/Tank |
| Delivery Period: | 15 days |
| Payment Method: | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Capacity: | 5000kg/month |
Methane gas (CH4) is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable hydrocarbon gas. It is the simplest and most abundant hydrocarbon compound. Here are some key points about methane gas:
Chemical Composition: Methane is composed of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms (CH4).
Properties: Methane possesses several important properties:
Flammability: Methane is highly flammable, and it can combust in the presence of an ignition source and sufficient oxygen. It is the primary component of natural gas, which is widely used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and electricity generation.
Greenhouse Gas: Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, meaning it has a significant impact on Earth's climate system. It has a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide over a 20-year timeframe, although it has a shorter lifespan in the atmosphere.
Odorless and Colorless: Pure methane gas is odorless and colorless. However, an odorant called mercaptan is often added to natural gas for safety reasons, to help detect leaks by giving it a distinctive smell.
Low Boiling Point: Methane has a boiling point of approximately -161.5 degrees Celsius (-258.7 degrees Fahrenheit) at atmospheric pressure.
Occurrence and Sources: Methane occurs naturally and is produced by both biological and non-biological processes:
Natural Sources: Methane is generated in various natural environments, including wetlands, rice paddies, landfills, and the digestive systems of ruminant animals (such as cows).
Fossil Fuels: Methane is the main component of natural gas, which is found underground and is extracted for use as a fuel source. It is also released during the extraction, production, and distribution of coal, oil, and natural gas.
Anthropogenic Sources: Human activities, such as agriculture, livestock farming, coal mining, wastewater treatment, and the burning of fossil fuels, contribute to the release of methane into the atmosphere.
Environmental Impact: Methane has significant implications for climate change and air quality:
Climate Change: Methane is a potent greenhouse gas. Its increased concentration in the atmosphere contributes to global warming and climate change, as it absorbs and traps heat radiating from the Earth's surface.
Air Quality: Methane also plays a role in air pollution. Incomplete combustion of methane can lead to the production of other pollutants, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, which have adverse effects on human health and the environment.
Uses: Methane gas has several important applications:
Energy Source: Methane is a valuable fuel source used for heating, cooking, electricity generation, and as a feedstock for the production of chemicals and fertilizers.
Industrial Processes: Methane is used as a raw material in various industrial processes, including the production of hydrogen, methanol, and other chemicals.
Transportation: Methane can also be used as a fuel for vehicles, either directly as compressed natural gas (CNG) or as a liquefied form (LNG).
Biogas: Methane produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic waste, such as agricultural waste or sewage, can be captured and used as biogas for energy generation.
Efforts are underway to mitigate methane emissions and develop more sustainable practices, such as improving methane capture and utilization, reducing leaks in natural gas infrastructure, and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
| Molecular Weight | 16.043 | Density | 0.717G/L |
| Melting Point | -182.5ºC | Boiling Point | -161.5ºC |
| Appearance | Colorless,Odorless | Un No. | 1971 |
| DOT Class | 2.1 | Valve | CGA350 |
| Cylinder Standard | DOT/ISO/GB | Cylinder Pressure | 15Mpa/20Mpa |
| Transport Package | 40L/47L/50L | Specification | 99.9%,99.99%,99.999% |
| Trademark | CMC | Origin | China |
| HS Code | 27112900 | Production Capacity | 20000m³/Year |
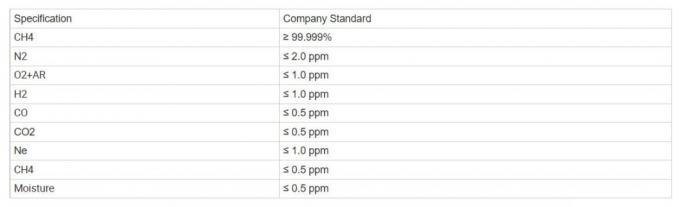
Specification:







| MOQ: | 1kg |
| Price: | US $15/kg |
| Standard Packaging: | Cylinder/Tank |
| Delivery Period: | 15 days |
| Payment Method: | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Capacity: | 5000kg/month |
Methane gas (CH4) is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable hydrocarbon gas. It is the simplest and most abundant hydrocarbon compound. Here are some key points about methane gas:
Chemical Composition: Methane is composed of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms (CH4).
Properties: Methane possesses several important properties:
Flammability: Methane is highly flammable, and it can combust in the presence of an ignition source and sufficient oxygen. It is the primary component of natural gas, which is widely used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and electricity generation.
Greenhouse Gas: Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, meaning it has a significant impact on Earth's climate system. It has a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide over a 20-year timeframe, although it has a shorter lifespan in the atmosphere.
Odorless and Colorless: Pure methane gas is odorless and colorless. However, an odorant called mercaptan is often added to natural gas for safety reasons, to help detect leaks by giving it a distinctive smell.
Low Boiling Point: Methane has a boiling point of approximately -161.5 degrees Celsius (-258.7 degrees Fahrenheit) at atmospheric pressure.
Occurrence and Sources: Methane occurs naturally and is produced by both biological and non-biological processes:
Natural Sources: Methane is generated in various natural environments, including wetlands, rice paddies, landfills, and the digestive systems of ruminant animals (such as cows).
Fossil Fuels: Methane is the main component of natural gas, which is found underground and is extracted for use as a fuel source. It is also released during the extraction, production, and distribution of coal, oil, and natural gas.
Anthropogenic Sources: Human activities, such as agriculture, livestock farming, coal mining, wastewater treatment, and the burning of fossil fuels, contribute to the release of methane into the atmosphere.
Environmental Impact: Methane has significant implications for climate change and air quality:
Climate Change: Methane is a potent greenhouse gas. Its increased concentration in the atmosphere contributes to global warming and climate change, as it absorbs and traps heat radiating from the Earth's surface.
Air Quality: Methane also plays a role in air pollution. Incomplete combustion of methane can lead to the production of other pollutants, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, which have adverse effects on human health and the environment.
Uses: Methane gas has several important applications:
Energy Source: Methane is a valuable fuel source used for heating, cooking, electricity generation, and as a feedstock for the production of chemicals and fertilizers.
Industrial Processes: Methane is used as a raw material in various industrial processes, including the production of hydrogen, methanol, and other chemicals.
Transportation: Methane can also be used as a fuel for vehicles, either directly as compressed natural gas (CNG) or as a liquefied form (LNG).
Biogas: Methane produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic waste, such as agricultural waste or sewage, can be captured and used as biogas for energy generation.
Efforts are underway to mitigate methane emissions and develop more sustainable practices, such as improving methane capture and utilization, reducing leaks in natural gas infrastructure, and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
| Molecular Weight | 16.043 | Density | 0.717G/L |
| Melting Point | -182.5ºC | Boiling Point | -161.5ºC |
| Appearance | Colorless,Odorless | Un No. | 1971 |
| DOT Class | 2.1 | Valve | CGA350 |
| Cylinder Standard | DOT/ISO/GB | Cylinder Pressure | 15Mpa/20Mpa |
| Transport Package | 40L/47L/50L | Specification | 99.9%,99.99%,99.999% |
| Trademark | CMC | Origin | China |
| HS Code | 27112900 | Production Capacity | 20000m³/Year |
Specification:







