


| MOQ: | 1 m3 |
| Price: | US $3/m3 |
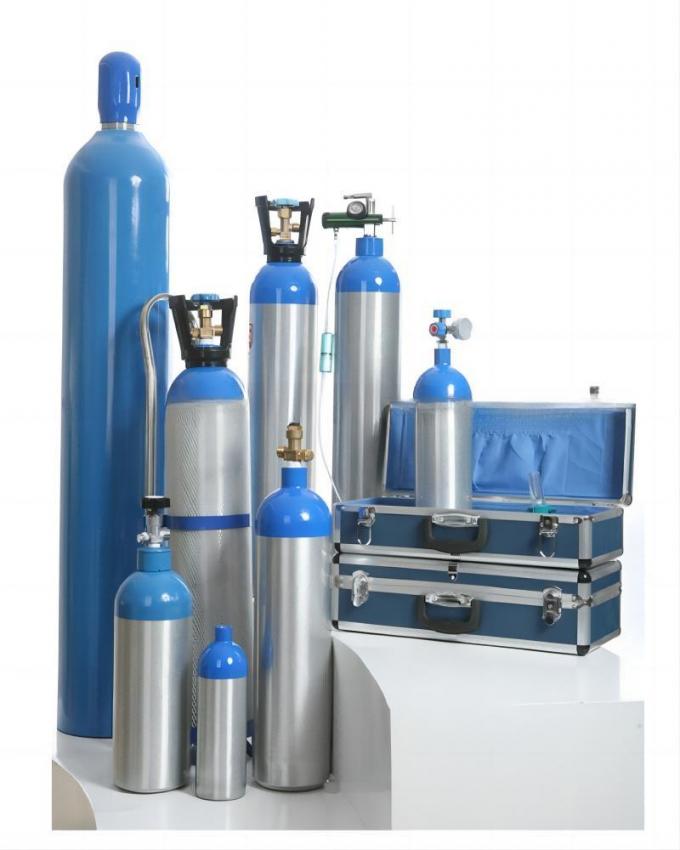
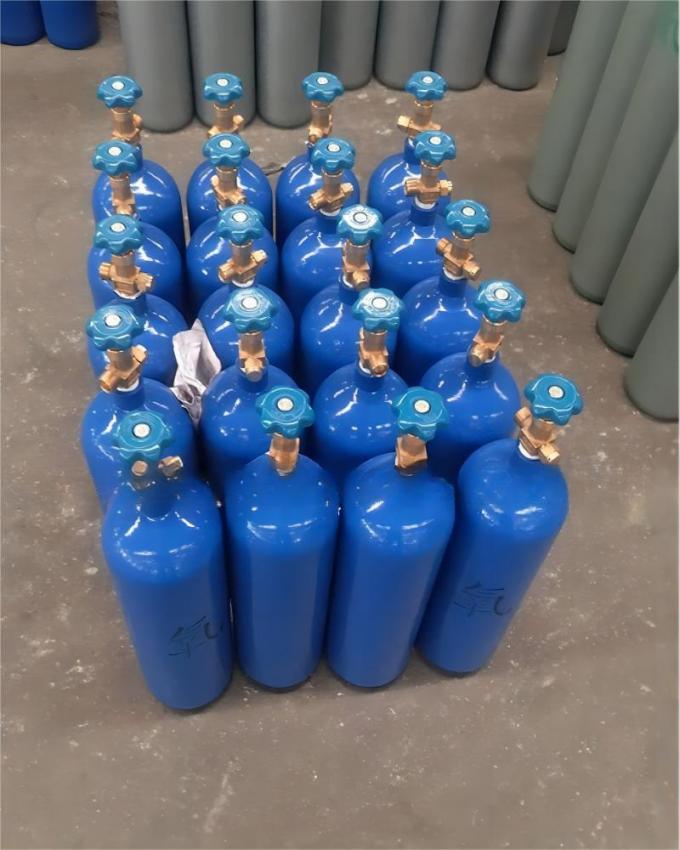
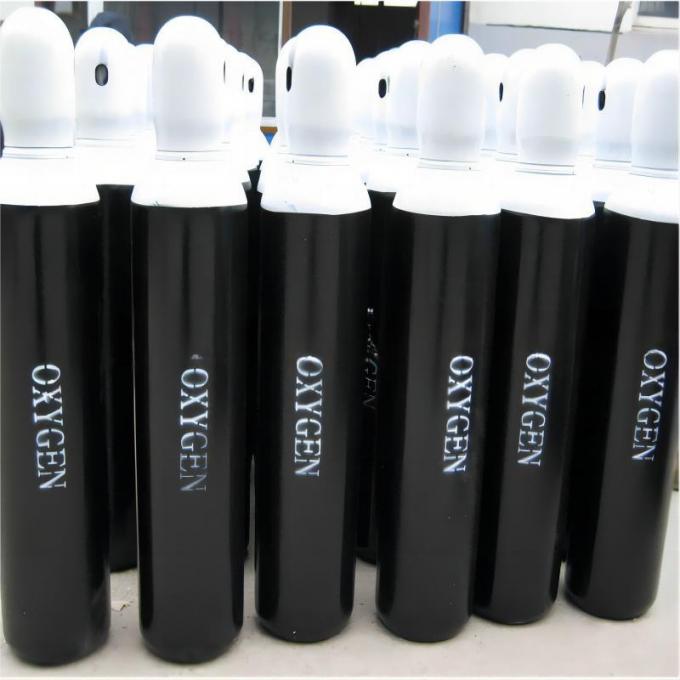
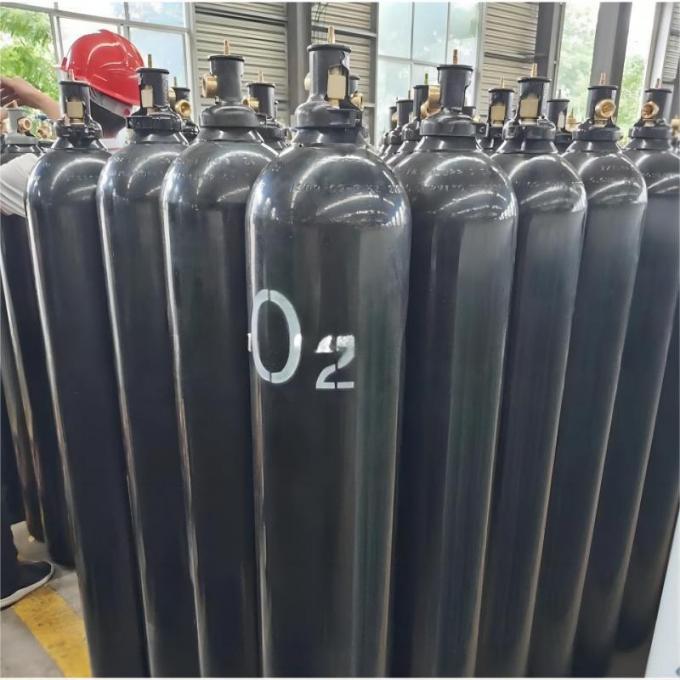
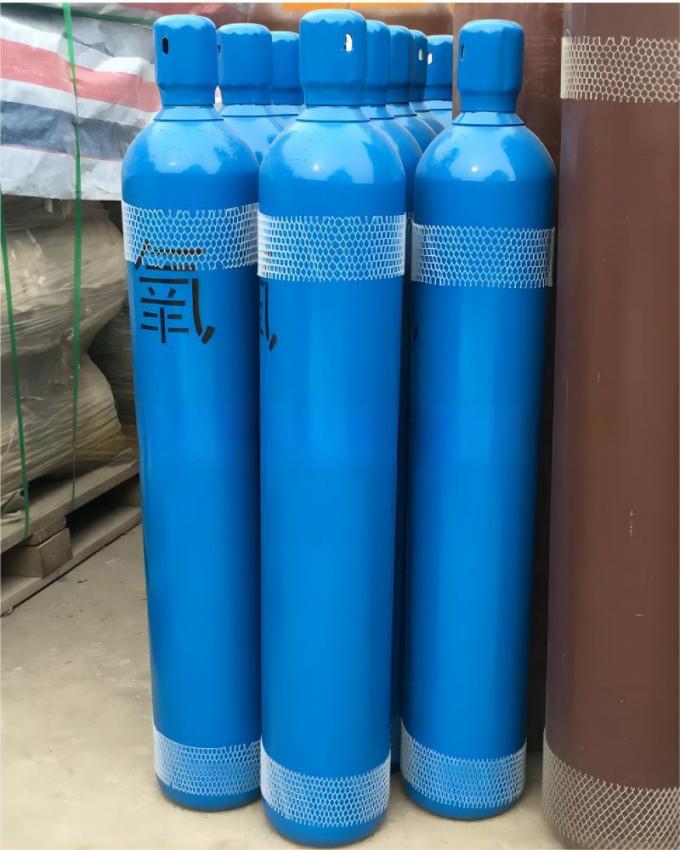
| Standard Packaging: | Cylinder |
| Delivery Period: | 15 days |
| Payment Method: | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Capacity: | 1000Tons/year |
Oxygen gas, often referred to simply as oxygen (O2), is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is essential for supporting life on Earth. It is one of the most abundant elements in the Earth's atmosphere, making up about 21% of the air we breathe.
Oxygen gas is composed of two oxygen atoms bonded together by a covalent bond, forming a diatomic molecule (O2). It is highly reactive and readily participates in chemical reactions. Its reactivity and ability to support combustion make it a vital component in various industrial processes, from metal smelting to the production of chemicals and fuels.
In biological systems, oxygen gas plays a crucial role in cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy. During respiration, oxygen is used by cells to break down glucose and other organic molecules to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. Without oxygen, most organisms, including humans, would not be able to survive.
Oxygen gas can be produced through various methods, including electrolysis of water, fractional distillation of liquefied air, and chemical reactions. It is commonly stored and transported in compressed gas cylinders or as a cryogenic liquid at very low temperatures.
Medical oxygen, which is used for therapeutic purposes, is a high-purity form of oxygen gas produced to meet specific standards for safety and purity. It is used in hospitals, clinics, and homecare settings to support patients with respiratory conditions and to aid in medical procedures.
Oxygen gas is also used in other industries, such as welding, cutting, and laser technologies. It is a vital component in the combustion of fuels, such as in the aerospace industry for rocket propulsion and in the steel industry for blast furnace operations.
It is important to note that while oxygen is crucial for sustaining life, it can also be hazardous in certain situations. Oxygen supports combustion, and high concentrations of oxygen can increase the flammability of materials and potentially lead to fires or explosions. Special precautions should be taken when handling and storing oxygen gas to ensure safety.
| Transport Package: | 40L/47L/50L/ISO Tank | Melting Point | -218.4 ºC |
| Trademark: | CMC | Boiling Point | -183 ºC |
| Specification | 99.999% | Production Capacity | 100, 000m3/Year |
| Cylinder Pressure | 12.5MPa/15MPa/20MPa | Valve | Qf-2/Cga580 |
| Appearance | Colorless, Odorless | Density | 1.429g/L |
Specification:
CAS No.: 7782-44-7
EINECS No.: 231-956-9
UN No.: UN1072
Purity: 99.999%-99.9999%
Dot Class: 2.2 & 5.1
Appearance: Colorless
Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, Grade, Electronic Grade
| Specification | 99.999% |
| Hydrogen | ≤0.5 ppm |
| Argon | ≤2 ppm |
| Nitrogen | ≤5 ppm |
| Carbon Dioxide | ≤0.5 ppm |
| THC (as CH4) | ≤0.5 ppm |
| Moisture | ≤2 ppm |
| Cylinder Specifications | Contents | Pressure | ||
| Cylinder Capacity | Valve | Volume | bar | psig |
| 40L | QF-2 | 7 m3 | 150 | 2175 |
| 47L | QF-2 | 7 m3 | 150 | 2175 |
| 50L | QF-2 | 10 m3 | 200 | 2900 |








| MOQ: | 1 m3 |
| Price: | US $3/m3 |
| Standard Packaging: | Cylinder |
| Delivery Period: | 15 days |
| Payment Method: | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Capacity: | 1000Tons/year |
Oxygen gas, often referred to simply as oxygen (O2), is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is essential for supporting life on Earth. It is one of the most abundant elements in the Earth's atmosphere, making up about 21% of the air we breathe.
Oxygen gas is composed of two oxygen atoms bonded together by a covalent bond, forming a diatomic molecule (O2). It is highly reactive and readily participates in chemical reactions. Its reactivity and ability to support combustion make it a vital component in various industrial processes, from metal smelting to the production of chemicals and fuels.
In biological systems, oxygen gas plays a crucial role in cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy. During respiration, oxygen is used by cells to break down glucose and other organic molecules to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. Without oxygen, most organisms, including humans, would not be able to survive.
Oxygen gas can be produced through various methods, including electrolysis of water, fractional distillation of liquefied air, and chemical reactions. It is commonly stored and transported in compressed gas cylinders or as a cryogenic liquid at very low temperatures.
Medical oxygen, which is used for therapeutic purposes, is a high-purity form of oxygen gas produced to meet specific standards for safety and purity. It is used in hospitals, clinics, and homecare settings to support patients with respiratory conditions and to aid in medical procedures.
Oxygen gas is also used in other industries, such as welding, cutting, and laser technologies. It is a vital component in the combustion of fuels, such as in the aerospace industry for rocket propulsion and in the steel industry for blast furnace operations.
It is important to note that while oxygen is crucial for sustaining life, it can also be hazardous in certain situations. Oxygen supports combustion, and high concentrations of oxygen can increase the flammability of materials and potentially lead to fires or explosions. Special precautions should be taken when handling and storing oxygen gas to ensure safety.
| Transport Package: | 40L/47L/50L/ISO Tank | Melting Point | -218.4 ºC |
| Trademark: | CMC | Boiling Point | -183 ºC |
| Specification | 99.999% | Production Capacity | 100, 000m3/Year |
| Cylinder Pressure | 12.5MPa/15MPa/20MPa | Valve | Qf-2/Cga580 |
| Appearance | Colorless, Odorless | Density | 1.429g/L |
Specification:
CAS No.: 7782-44-7
EINECS No.: 231-956-9
UN No.: UN1072
Purity: 99.999%-99.9999%
Dot Class: 2.2 & 5.1
Appearance: Colorless
Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, Grade, Electronic Grade
| Specification | 99.999% |
| Hydrogen | ≤0.5 ppm |
| Argon | ≤2 ppm |
| Nitrogen | ≤5 ppm |
| Carbon Dioxide | ≤0.5 ppm |
| THC (as CH4) | ≤0.5 ppm |
| Moisture | ≤2 ppm |
| Cylinder Specifications | Contents | Pressure | ||
| Cylinder Capacity | Valve | Volume | bar | psig |
| 40L | QF-2 | 7 m3 | 150 | 2175 |
| 47L | QF-2 | 7 m3 | 150 | 2175 |
| 50L | QF-2 | 10 m3 | 200 | 2900 |







